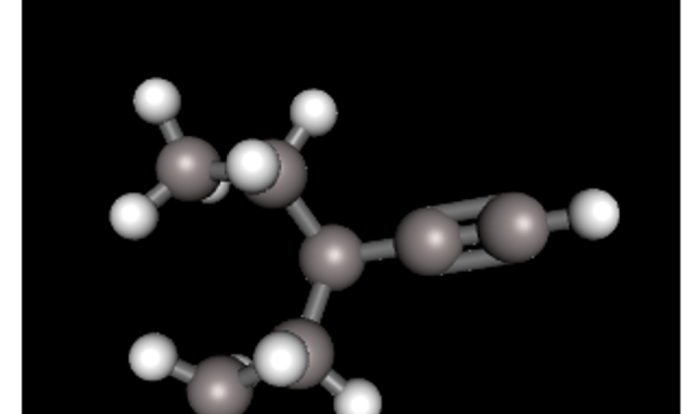
Draw the most stable lewis structure of acrolein. – In the realm of chemistry, understanding the electronic structure of molecules is crucial. Lewis structures, a powerful tool in this endeavor, provide a visual representation of the arrangement of atoms and electrons within a molecule. This article embarks on an in-depth exploration of drawing the most stable Lewis structure of acrolein, a highly reactive and versatile compound with significant implications in various fields.
Acrolein, with the molecular formula C3H4O, is an unsaturated aldehyde characterized by its pungent, irritating odor. Its chemical structure consists of a carbon-carbon double bond and a carbonyl group, making it a highly reactive species. Understanding the Lewis structure of acrolein is essential for comprehending its chemical behavior and reactivity.
Introduction to Acrolein
Acrolein, also known as propenal, is a toxic, colorless liquid with a pungent odor. It is the simplest unsaturated aldehyde and has the chemical formula CH 2=CHCHO. Acrolein is an important intermediate in the production of many chemicals, including acrylic acid and methacrylic acid, which are used in the manufacture of plastics, paints, and adhesives.
Lewis Structure of Acrolein

A Lewis structure is a diagram that shows the arrangement of electrons in a molecule. To draw a Lewis structure, first determine the total number of valence electrons in the molecule. Acrolein has six valence electrons: two from each carbon atom, four from the oxygen atom, and one from the hydrogen atom.
Next, connect the atoms with single bonds. Each single bond represents two electrons. In acrolein, the carbon atoms are connected to each other with a single bond, and the carbon atom that is double-bonded to the oxygen atom is also connected to the hydrogen atom with a single bond.
Finally, distribute the remaining electrons as lone pairs. In acrolein, the oxygen atom has two lone pairs of electrons.
The Lewis structure of acrolein is shown below:
H2C=CH-CHO
Resonance in Acrolein
Resonance is a phenomenon that occurs when two or more Lewis structures can be drawn for a molecule. In acrolein, there are two resonance structures:
H2C=CH-CHO ↔ -CH 2-CH=O +
The two resonance structures are equivalent, meaning that they have the same energy. The actual structure of acrolein is a hybrid of the two resonance structures.
Hybridization of Acrolein
Hybridization is the mixing of atomic orbitals to form new orbitals with different shapes and energies. In acrolein, the carbon atom that is double-bonded to the oxygen atom is sp 2hybridized. This means that it has three sp 2hybrid orbitals and one p orbital.
The sp 2hybrid orbitals are used to form the sigma bonds with the other atoms in the molecule, and the p orbital is used to form the pi bond with the oxygen atom.
The hybridization of the carbon atom affects the molecular geometry of acrolein. The sp 2hybrid orbitals are arranged in a trigonal planar geometry, which means that the three atoms that are bonded to the carbon atom are in a plane.
The p orbital is perpendicular to the plane of the sp 2hybrid orbitals.
Polarity of Acrolein
Polarity is a measure of the separation of electric charge within a molecule. A molecule is polar if it has a positive end and a negative end. The polarity of a molecule is determined by the electronegativity of the atoms in the molecule.
Electronegativity is a measure of the ability of an atom to attract electrons. The more electronegative an atom, the more strongly it attracts electrons.
In acrolein, the oxygen atom is more electronegative than the carbon atoms. This means that the oxygen atom attracts electrons more strongly than the carbon atoms. As a result, the electrons in the C=O bond are pulled towards the oxygen atom, creating a partial positive charge on the carbon atom and a partial negative charge on the oxygen atom.
The polarity of acrolein can be calculated using the dipole moment. The dipole moment is a measure of the separation of electric charge within a molecule. The dipole moment of acrolein is 3.7 D. This indicates that acrolein is a polar molecule.
Applications of Acrolein: Draw The Most Stable Lewis Structure Of Acrolein.
Acrolein is used in the production of a variety of chemicals, including acrylic acid, methacrylic acid, and acrolein resins. Acrylic acid is used in the production of plastics, paints, and adhesives. Methacrylic acid is used in the production of plexiglass and other clear plastics.
Acrolein resins are used in the production of coatings and adhesives.
Acrolein is also used as a fumigant and a herbicide. As a fumigant, acrolein is used to kill insects and rodents in stored products. As a herbicide, acrolein is used to control weeds in crops.
Popular Questions
What is the significance of drawing the most stable Lewis structure?
Drawing the most stable Lewis structure is crucial for predicting the chemical behavior and reactivity of a molecule. It provides insights into the distribution of electrons, the hybridization of atoms, and the molecular geometry, which are essential for understanding chemical reactions and properties.
How does resonance affect the stability of acrolein’s Lewis structure?
Resonance occurs when there are multiple possible Lewis structures for a molecule. In the case of acrolein, resonance structures contribute to its stability by delocalizing the electrons, reducing the overall energy of the molecule.
What is the hybridization of the carbon atoms in acrolein?
The carbon atoms in acrolein are sp2 hybridized. This hybridization results in a trigonal planar molecular geometry around each carbon atom, with the double bond and the carbonyl group lying in the same plane.