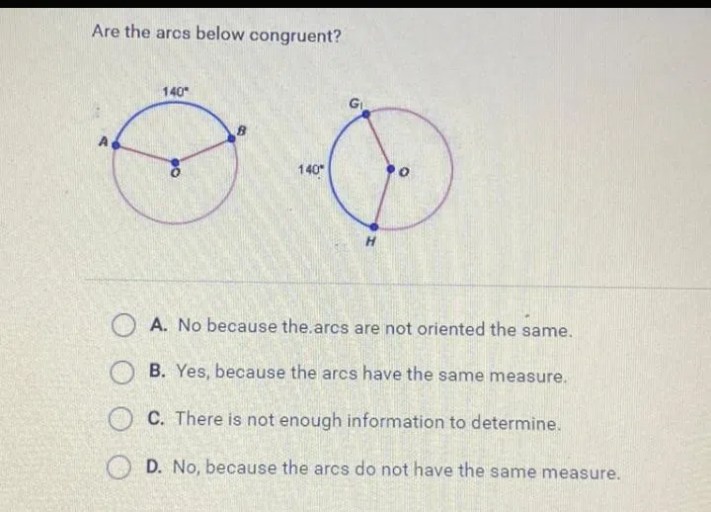
Which arc is congruent to eh – Embark on an intellectual journey as we delve into the captivating world of arc congruence, where arcs share a harmonious equality. This comprehensive guide will illuminate the concepts, methods, and applications of arc congruence, unraveling its significance in geometry and beyond.
Prepare to be captivated as we explore the intricacies of arc congruence, unraveling its properties and unlocking its applications in various mathematical realms. Get ready to witness the elegance of congruent arcs as they unveil the secrets of geometric harmony.
Concepts of Arc Congruence
Arc congruence refers to the equivalence in measure between two arcs. Congruent arcs are those that have the same length, regardless of the radii of the circles they belong to. The concept of arc congruence is essential in geometry for determining the equality of various geometric shapes and figures.
Properties of Congruent Arcs
- Equal Length:The most fundamental property of congruent arcs is their equal length. They have the same measure in degrees or radians.
- Subtend Equal Central Angles:Congruent arcs subtend equal central angles at the center of the circle. The central angle is the angle formed by the radii drawn from the center of the circle to the endpoints of the arc.
- Equal Radii:If two congruent arcs belong to the same circle, they have equal radii. This property follows from the definition of arc congruence.
- Interchangeable:Congruent arcs can be interchanged without affecting the congruence of the figure. This means that if two arcs are congruent, they can be replaced by each other without altering the geometric properties of the figure.
Examples of Congruent Arcs, Which arc is congruent to eh
Consider two circles with radii rand R, respectively. Let Aand Bbe two points on the circumference of the smaller circle, and let Cand Dbe two points on the circumference of the larger circle. If the arc ABis congruent to the arc CD, then the following properties hold:
- The measure of arc ABis equal to the measure of arc CD.
- The central angle ∠ AOBis equal to the central angle ∠ COD.
- The radii rand Rare not necessarily equal.
Methods for Determining Arc Congruence
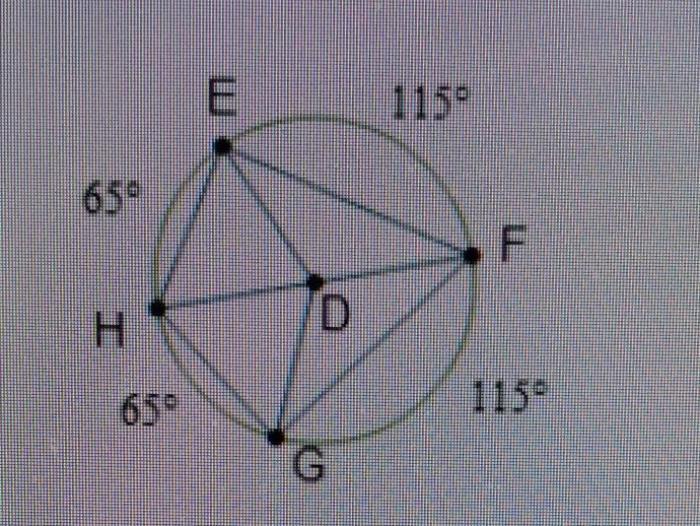
Determining whether two arcs are congruent requires careful measurements and analysis. This section explores various methods for measuring arcs and comparing their measures to establish congruence.
Measuring Arcs
Measuring arcs involves using a protractor or other angle-measuring devices. Here’s how it’s done:
- Place the protractor’s center at the center of the circle.
- Align the protractor’s baseline with one of the radii passing through the endpoints of the arc.
- Read the measure of the arc from the protractor’s scale.
Comparing Arc Measures
Once the arcs are measured, comparing their measures determines their congruence. Two arcs are congruent if they have the same measure in degrees.
For example, if Arc AB measures 60 degrees and Arc CD measures 60 degrees, then Arc AB is congruent to Arc CD.
Role of Central Angles in Arc Congruence
Central angles play a crucial role in determining arc congruence. A central angle is an angle whose vertex is at the center of the circle and whose sides pass through the endpoints of the arc.
Theorem: If two arcs are intercepted by congruent central angles, then the arcs are congruent.
This theorem provides a convenient way to establish arc congruence without directly measuring the arcs.
While exploring the intriguing world of geometry, you might stumble upon the concept of congruent arcs. As you delve deeper into this topic, you’ll encounter a scenario that may seem as unexpected as a mugger stealing your wallet . Just as a mugger can swiftly snatch your belongings, the realization that certain arcs are congruent can come as a sudden and surprising revelation.
Applications of Arc Congruence in Geometry
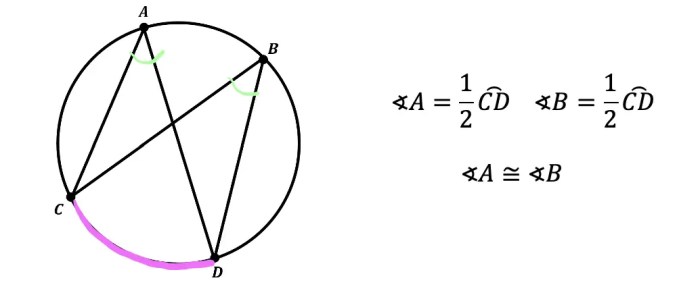
Arc congruence plays a crucial role in proving triangles congruent and in various constructions and theorems in circle geometry.
Proving Triangles Congruent
Arc congruence is used to establish the congruence of triangles by proving the equality of their corresponding parts. One common method is the Angle-Side-Angle (ASA) congruence theorem, which states that if two triangles have two congruent angles and a congruent side between them, then the triangles are congruent.
In this theorem, the congruence of arcs can be used to prove the congruence of angles, which in turn helps establish the triangle’s congruence.
Theorems and Constructions
Arc congruence is also utilized in theorems and constructions related to circles. For example, the Inscribed Angle Theorem states that the measure of an inscribed angle is half the measure of its intercepted arc. This theorem allows for the determination of arc lengths and angle measures in circles.
Additionally, arc congruence is employed in constructing regular polygons inscribed in circles, ensuring that the arcs subtended by the polygon’s sides are congruent.
Significance in Circle Geometry
Arc congruence is a fundamental concept in circle geometry. It establishes relationships between arcs, angles, and chords, providing a framework for understanding and solving problems involving circles. By understanding the properties of congruent arcs, geometers can analyze and construct various figures within circles, such as inscribed and circumscribed polygons, and determine their properties.
Advanced Topics in Arc Congruence

As we delve deeper into the realm of arc congruence, we uncover intricate relationships with angle congruence, intercepted arcs, and their profound applications in trigonometry and calculus.
Relationship between Arc Congruence and Angle Congruence
Arc congruence and angle congruence are closely intertwined. When two arcs are congruent, the central angles that intercept them are also congruent. Conversely, if two central angles are congruent, the arcs they intercept are congruent. This relationship forms the cornerstone of many geometric proofs and constructions.
Intercepted Arcs
Intercepted arcs are arcs that lie between two radii or chords of a circle. The length of an intercepted arc is directly proportional to the measure of its central angle. This concept plays a crucial role in understanding circle geometry and calculating arc lengths.
Applications in Trigonometry and Calculus
Arc congruence finds numerous applications in trigonometry. By establishing relationships between arcs and angles, we can derive trigonometric identities and solve trigonometric equations. In calculus, arc congruence allows us to calculate arc lengths and areas of sectors, which are essential for integration and differential geometry.
Answers to Common Questions: Which Arc Is Congruent To Eh
What is arc congruence?
Arc congruence is a relationship between two arcs that have the same measure, meaning they span the same portion of their respective circles.
How do you determine if two arcs are congruent?
To determine if two arcs are congruent, you can compare their measures directly or use the properties of central angles to establish their congruence.
What are the applications of arc congruence in geometry?
Arc congruence plays a crucial role in proving triangles congruent, constructing geometric figures, and understanding the relationships within circles.